Full-Stack Web Development, according to the Stack Overflow 2016 Developer Survey,
is the most popular developer occupation today. It’s no wonder then
that there are dozens of online and in-person programs that will help
people become Full-Stack Developers and then even assist these new
developers land high-paying programming jobs.
Some popular online programs can be found on Lynda, Udacity, Coursera, Thinkful, General Assembly, and so much more. Aside from these online programs, there are also in-person coding bootcamps that are teaching people the skills required to become web developers.
In
this article I won’t be discussing which websites or coding bootcamps
have the best web development programs, instead I will be providing a definitive guide to what I believe are the most important skills
required to become a Full-Stack Web Developer today and land a job if
you’ve never coded before. I will be basing the list off of three
things:
- A combination of what most programs in 2017 are teaching students.
- My own personal experiences from interviewing at companies for developer positions in the past and also interviewing potential candidates for current Full-Stack Developer positions at my current company.
- Stories and feedback from people on Coderbyte who have been accepted to coding bootcamps and then proceeded to get programming jobs (see below).
The Definitive Guide
A Full-Stack Web Developer is someone who is able to work
on both the front-end and back-end portions of an application.
Front-end generally refers to the portion of an application the user
will see or interact with, and the back-end is the part of the
application that handles the logic, database interactions, user
authentication, server configuration, etc. Being a Full-Stack Developer doesn’t mean that you have necessarily mastered everything required to work with the front-end or back-end, but it means that you are able to work on both sides and understand what is going on when building an application.
If
you want to become a Full-Stack Web Developer in 2017 and land your
first job, below is a reference guide with a list of things you should
learn.
1. HTML/CSS

Almost
every single program, whether online or in-person, that is teaching you
how to be a web developer will start with HTML and CSS because they are
the building blocks of the web. Simply put, HTML allows you to add
content to a website and CSS is what allows you to style your content.
The following topics related to HTML/CSS come up often in interviews and
on the actual job when you’re working:
- Semantic HTML.
- Be able to explain the CSS Box Model.
- Benefits of CSS preprocessors (you don’t necessarily need to understand how to use one on a deep level, but you should to understand what they are for and how they help with development).
- CSS Media Queries to target different devices and write responsive CSS.
- Bootstrap (a framework for helping design and layout content on a page and while many online programs or schools focus heavily on teaching Bootstrap, in reality it’s more important to have a deep knowledge of fundamental CSS than specific Bootstrap features and methods).
2. JavaScript

The
JavaScript language is growing more popular every year and new
libraries, frameworks, and tools are constantly being released. Based on
the Stack Overflow 2016 Developer Survey,
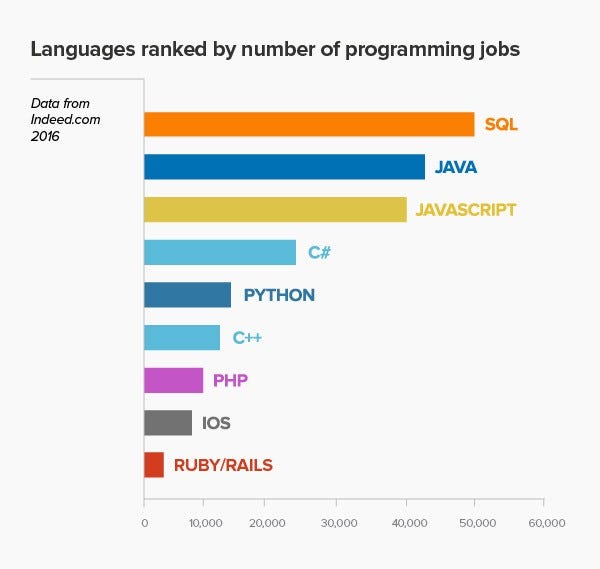
JavaScript is the most popular language in both Full-Stack, Front-end,
and Back-end Development. It’s the only language that runs natively in
the browser, and can double up as a server-side language as well (as
you’ll see below with Node.js). Below are some topics you need to
understand as a Full-Stack Developer:
- Understand how to work with the DOM. Also know what JSON is and how to manipulate it.
- Important language features such as functional composition, prototypal inheritance, closures, event delegation, scope, higher-order functions.
- Asynchronous control flow, promises, and callbacks.
- Learn how to properly structure your code and modularize parts of it, things like webpack, browserify, or build tools like gulp will definitely be helpful to know.
- Know how to use at least one popular framework (many programs will focus heavily on teaching you a library or framework like React or AngularJS, but in reality it’s much more important to have a deep understanding of the JavaScript language and not focus so much on framework-specific features. Once you have a good understanding of JavaScript, picking up a framework that sits on top of it won’t be too hard anyway).
- Although some may argue that you should be using this less or that it’s slowly dying, jQuery code still exists in most applications and a solid understanding of it will be helpful.
- Some knowledge on testing frameworks and why they’re important (some may even claim that this topic should be optional).
- Learn about some important new ES6 features (optional).
3. Back-End Language
Once
you feel you’ve gotten a good grasp on HTML/CSS and JavaScript, you’ll
want to move on to a back-end language that will handle things like
database operations, user authentication, and application logic. All
online programs and bootcamps usually focus on a specific back-end
language, and in reality in doesn’t matter which one you learn so much
as long as you understand what is going on and you learn the nuances of your chosen language. You’ll get a ton of different responses
if you ask someone which back-end language is the best to learn, so
below I’ve listed a few popular combinations. An important note:
whichever you decide to learn, just stick with it and learn as much as
you can about it — there are jobs out there for all the languages listed below.

- Node.js: This is a great option because Node.js is itself just a JavaScript environment which means you don’t need to learn a new language. This is a big reason why a lot of online programs and bootcamps choose to teach Node.js. The most popular framework you’d most likely learn to aid you in developing web applications is Express.
- Ruby: Some popular frameworks for developing in Ruby are Rails and Sinatra. Plenty of programs teach Ruby as a first back-end language.
- Python: Some popular frameworks for developing in Python are Django and Flask.
- Java: The Java language isn’t taught so much these days when it comes to Full-Stack Web Development, but some companies do use Java as their back-end and it is still a very in-demand language (see image above).
- PHP: PHP is rarely taught in programs these days, but just like with Java, it is still very in-demand and it is a cornerstone of the web today.
4. Databases & Web Storage

When
learning to build web applications, at some point you’ll probably want
to store data somewhere and then access it later. You should have a good
grasp on the following topics related to databases and storage.
- Understand the benefits of relational data, e.g. SQL.
- Learn about NoSQL databases, e.g. MongoDB.
- Understand which would be better in certain situations.
- Know how to connect a database with your chosen back-end language (e.g. Node.js + MongoDB).
- Understand the benefits of in-memory data stores like Redis or memcached.
- Web storage to store sessions, cookies, and cached data in the browser.
- Scaling databases, ACID, and ORM (all optional).
5. HTTP & REST
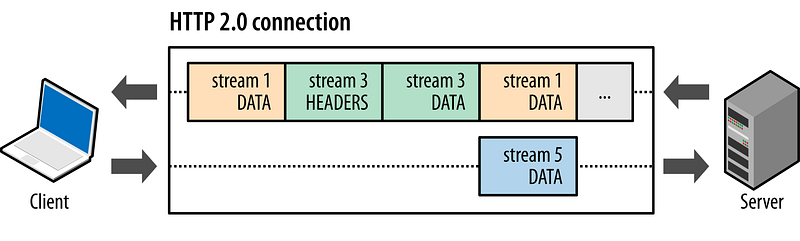
HTTP
is a stateless application protocol on the Internet — it’s what allows
clients to communicate with servers (e.g. your JavaScript code can make
an AJAX request to some back-end code you have running on a server which
will happen via HTTP). Some important topics you should learn about are
listed below:
- What is REST and why is it important in regards to the HTTP protocol and web applications.
- Best practices for designing a RESTful API. POST/GET requests.
- Learning how to use Chrome DevTools can be extremely helpful.
- What are SSL Certificates.
- HTTP/2 & SPDY (optional).
- WebSockets, Web Workers, and Service Workers (all optional).
6. Web Application Architecture

Once
you think you have a grasp on HTML/CSS, JavaScript, back-end
programming, databases, and HTTP/REST, then comes the tricky part. At
this point if you want to create a somewhat complex web application,
you’ll need to know how to structure your code, how to separate your
files, where to host your large media files, how to structure the data
in your database, where to perform certain computational tasks
(client-side vs server-side), and much more.
There
are best practices that you can read about online on, but the best way
to actually learn about application architecture is by working on a
large application yourself that contains several moving parts — or even better, working on a team and together developing a somewhat large/complex application.
This
is why, for example, someone with 7+ years of experience may not
necessarily know CSS or JavaScript better than someone with 2 years of
experience, but over all of those years they’ve presumably worked with
all sorts of different applications and websites and have learned how to architect and design applications (among learning other important things)
to be most efficient and can see the “big picture” when it comes to
development. Below are some things you can read that will help you learn
how to architect your web applications efficiently:
- Learn about common platforms as a service, e.g. Heroku and AWS. Heroku allows you to easily upload your code and have an application up and running with very little configuration or server maintenance and AWS offers dozens of products and services to help with storage, video processing, load balancing, and much more.
- Performance optimization for applications and modern browsers.
- Some opinions on what a web application architecture should include.
- Designing Web Applications by Microsoft.
- MVC.
- Most importantly though you should try to work on projects with people, look at codebases of popular projects on GitHub, and learn as much as you can from senior developers.
7. Git
Git is a version control system
that allows developers working on a team to keep track of all the
changes being made to a codebase. It’s important to know a few important
things related to Git so that you understand how to properly get the
latest code that you’ve missed, update parts of the code, make fixes,
and change other people’s code without breaking things. You should
definitely learn the concept behind Git and play around with it yourself.
- Here’s a reference list of some common git commands you’ll likely use.
- Here’s a tutorial on using Git and GitHub for beginners.
8. Basic Algorithms & Data Structures

This topic is somewhat polarizing in the development world because there are developers who don’t think there should be such a heavy
focus on computer science topics like tree traversal, sorting,
algorithm analysis, matrix manipulation, etc. in web development.
However, there are companies like Google that are notorious for asking these types of questions in their interviews. As someone said about the Front-End engineering interview at Google:
That said, as Ryan McGrath mentions, our front-end (FE) engineers are expected to have a solid CS background, like all our engineers.
While
there are companies that practically require applicants to have a
computer science degree or equivalent, there are plenty of companies
that will hire people
without this technical qualification if they can prove that they know
how to develop applications and show an understanding of the whole
domain. But part of being a competent developer and not writing
inefficient code or using the wrong tools is an understanding of some
basic algorithms and data structures and being able to analyze
trade-offs. So here are some things you should definitely learn:
- Improving your Algorithms & Data Structure Skills Article
- Study hash tables and try to understand them on a deeper level. This data structure underlies objects in JavaScript (dictionaries in Python and hashes in Ruby).
- Understand how trees and graphs can be beneficial as data structures.
- Understand the basics of Big-O analysis so you don’t do silly things like create a nested loop 3 levels down if you don’t need to!
- Know when to use an object vs an array and understand the trade-offs.
- Learn why caching is so important when working with a large amount of data. Also learn the pros and cons of in-memory vs disk storage.
- Learn the difference between queues and stacks.
It’ll
be hard work learning all of this, but it’s rewarding in the end and
Full-Stack Development is fun! Leave your comments below, and check out Coderbyte for some algorithm practice.
Hire Full Stack Developer for advanced web & mobile applications and complete client-side solutions. Their dedicated Full Stack Developer work as your extended team and are capable of building interactive apps. Their team of expert Full Stack developers provides creative and eye-catchy mobile and web application development services as per the latest designing trends.
ReplyDelete